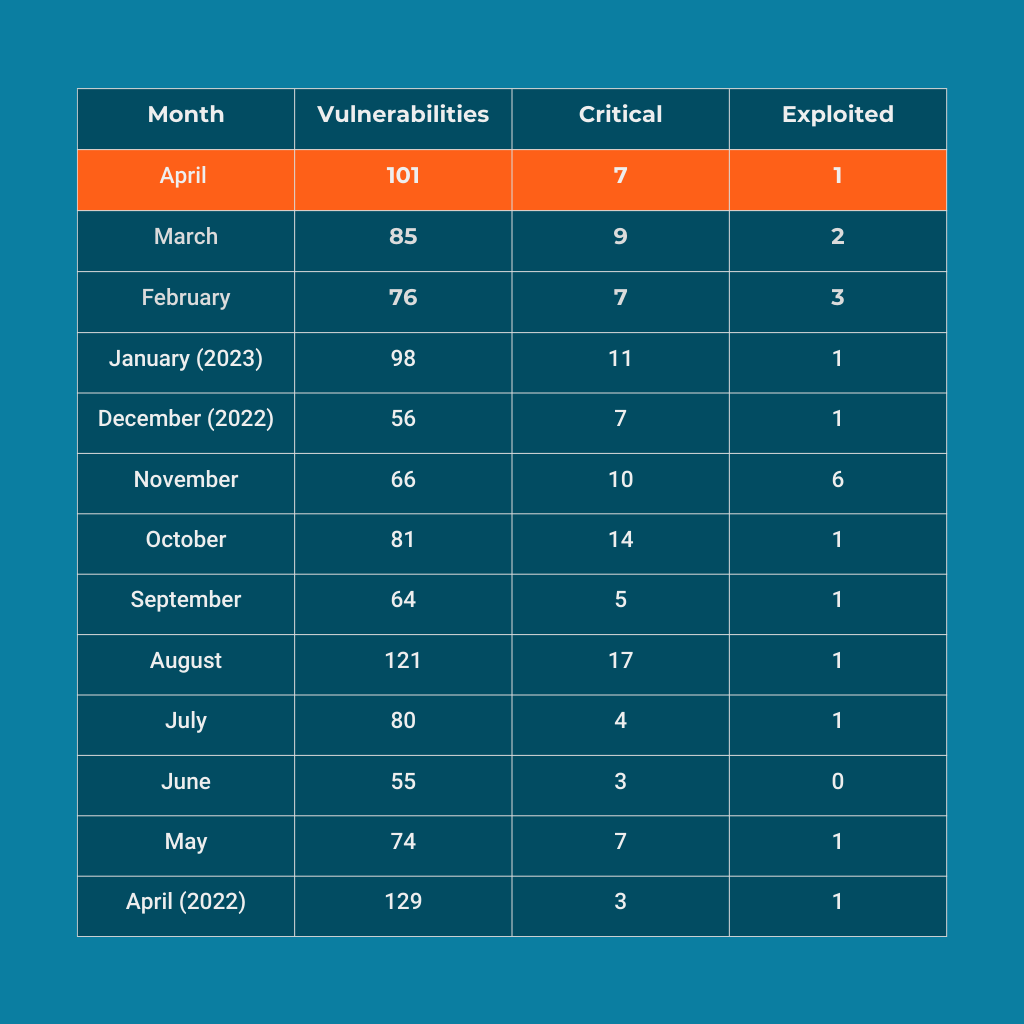
April’s Patch Tuesday release from Microsoft sees an additional zero-day fixed and a total of 101 vulnerabilities patched, 7 of them critical. The zero-day is a flaw in the Windows Common Log File System (CLFS) that allows elevation to SYSTEM privileges. This is the most vulnerabilities patched since August of 2022 in what will be a heavy month for administrators.
While zero-days usually get the headlines, this month’s release has a few critical vulnerabilities that shouldn’t be overlooked by administrators. The first is a critical CVSS 9.8/10 remote code execution vulnerability in Microsoft Message Queuing that affects Windows 10, 11, and Server 2008-2022. It’s likely to be exploited and should be patched within 24 hours on endpoints exposed to the internet.
The other high-priority vulnerability is a CVSS score 8.8/10 in the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) Server Service that allows an attacker with access to the restricted network to remotely execute code on the server. DHCP manages a record of all IP addresses, so attackers with access could deny service or direct DHCP clients to a malicious router. This vulnerability is likely to be targeted and exploited by attackers, and we recommend patching ASAP – ideally within 24 hours – as the impact of exploitation could be catastrophic.