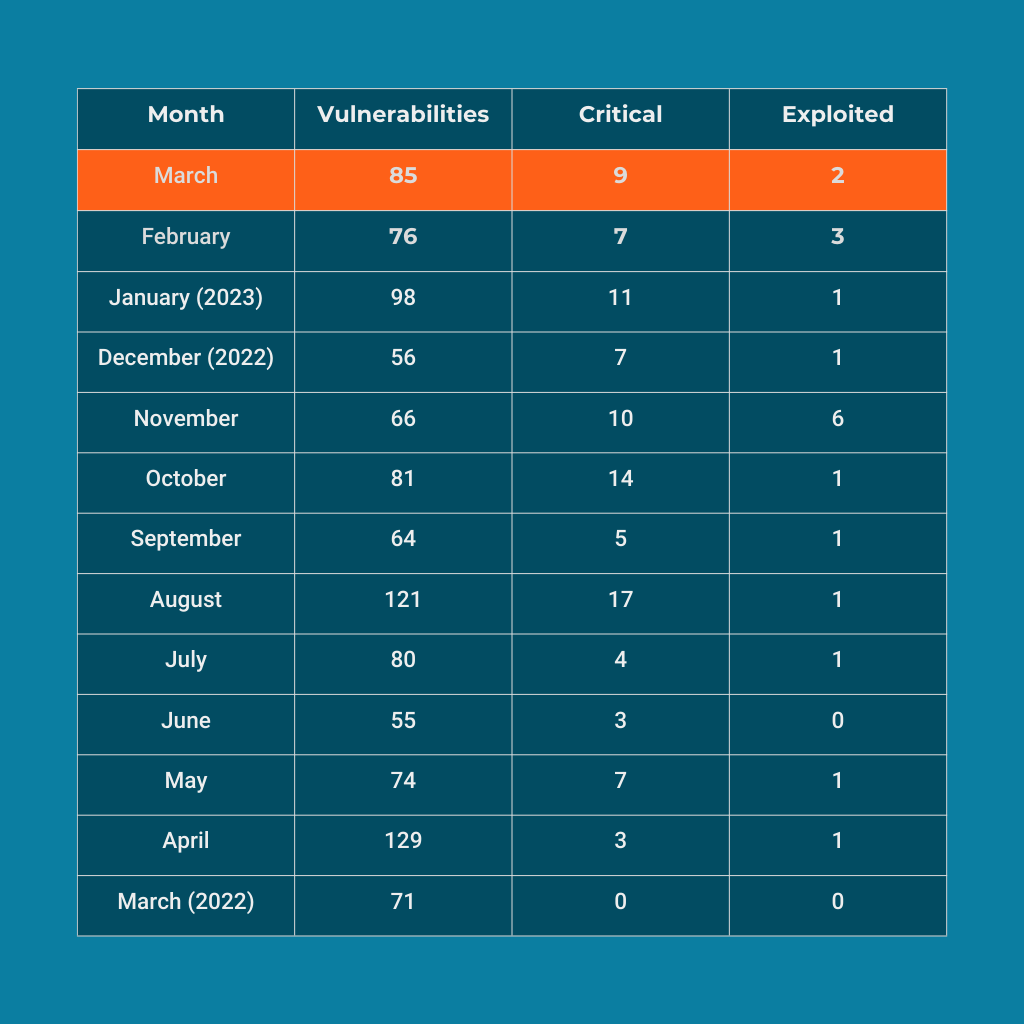
March’s Patch Tuesday release continues a streak of zero-days fixed by Microsoft that has lasted since June 2022. Two actively-exploited zero-day vulnerabilities were fixed this month, one in the near-ubiquitous Outlook application that allows attackers to spoof after stealing a user’s Net-NTLMv2 hash. The other is yet another security feature bypass in Windows SmartScreen.
On the whole, this month’s Patch Tuesday sees a total of 85 vulnerabilities patched, 9 of which are critical, and the two zero-days listed above. Of the critical vulnerabilities yet to be exploited, administrators should prioritize a critical, CVSSv3.1 9.8/10 remote code execution vulnerability affecting most Windows operating systems in the Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP).
In case you’re unfamiliar, remote code execution (RCE) is an attack where the attacker can access the device and execute malicious code. The impact of remote code execution can make the attacker gain complete control over the compromised machine.
There’s also a critical vulnerability in Windows Cryptographic Services affecting Windows 10, 11, and Server 2012 forward that allows for arbitrary code execution if an attacker can install or coerce the victim to install a malicious certificate on their device.